
Great Red Spot


The Moon, Jupiter and star Spica line up at dawn on 19 January
Before sunrise on Thursday 19 January, observers in Western Europe can see an interesting celestial conjunction in the southern sky. At about 6am local time, the waning gibbous Moon, largest planet Jupiter and Spica — the brightest star in the constellation of Virgo — all lie in a line encompassed by the field of view of a typical 7x or 8x binocular.


Waning crescent Moon joins Jupiter in the dawn sky of 25 November
Around 6:30am GMT on Friday 25 November, as nautical twilight starts for the centre of the UK, the 25-day-old waning crescent Moon lies just 2½ degrees away from largest planet Jupiter low in the southeastern sky. This juxtaposition of the two brightest objects in the dawn sky will be nicely framed in a typical binocular.

Jupiter’s Great Red Spot heats planet’s upper atmosphere
Astronomers from Boston University have discovered that Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS) may provide the mysterious source of energy required to heat the planet’s upper atmosphere to the unusually high values observed. Heating in Jupiter’s atmosphere 500 miles above the GRS is thought to be caused by gravity waves and acoustic waves creating turbulent atmospheric flows.

Hubble captures vivid aurorae in Jupiter’s atmosphere
Astronomers are using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope to study aurorae — stunning light shows in a planet’s atmosphere — on the poles of the largest planet in the solar system, Jupiter. This observation program is supported by measurements made by NASA’s Juno spacecraft, shortly to arrive at the gas giant.

Spectacular VLT images of Jupiter presented before Juno’s arrival
In preparation for the imminent arrival of NASA’s Juno spacecraft, astronomers have used ESO’s Very Large Telescope to obtain spectacular new infrared images of Jupiter as part of a campaign to create high-resolution maps of the giant planet. These observations will help astronomers to better understand the gas giant ahead of Juno’s close encounter next month.
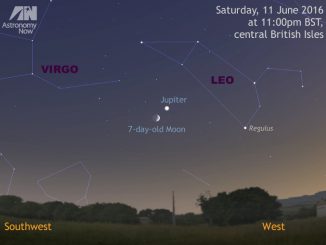
See the Moon and Jupiter get close on 11 June
As dusk fades to dark on Saturday, 11 June, observers in the British Isles should look low in the western sky to see the 7-day-old waxing crescent Moon and Jupiter less than 3 degrees apart, within the same binocular field of view. Get your observations in now as the solar system’s largest planet is poised to leave the celestial stage during the summer.
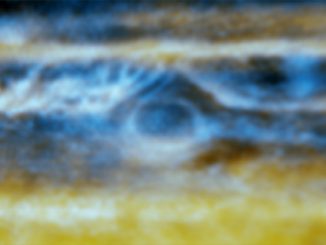
VLA radio map reveals what lies deep below Jupiter’s visible clouds
Observations with the National Science Foundation’s Very Large Array (VLA) have given astronomers an unprecedented look into the atmosphere of Jupiter. The scientists used the VLA to study the dynamics of Jupiter’s atmosphere from the visible cloud surfaces down to about 60 miles (100 kilometres) below the clouds.

Make the most of your Jupiter observations during May
Now two months past opposition, the solar system’s largest planet, Jupiter, is highest in the UK sky before sunset and is already descending in the southwest by the time the sky is dark enough to observe it. However, there is still phenomena of the Galilean moons to see and the planet’s Great Red Spot, so make the most of your Jovian observations while you can during May.
