
Ocean


Hubble spots possible water plumes erupting on Jupiter’s moon Europa
Astronomers using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have imaged what may be water vapour plumes erupting 125 miles (200 kilometres) off the surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa. Europa has a huge global ocean containing twice as much water as Earth’s oceans, but it is protected by a layer of extremely cold and hard ice of unknown thickness.

Saturn’s moon Enceladus and its paper-thin crust
Researchers have used data collected by the Cassini spacecraft to build a computer simulation of Saturn’s icy ocean moon Enceladus that includes the thickness of the ice crust. At its south poles, huge geysers of water jet into space. These come from the ocean depths and suggest that the ice there must be relatively thin for this to happen.

Mega-tsunamis ravaged shorelines of ancient Martian ocean
The geologic shape of what were once shorelines through Mars’ northern plains 3.4 billion years ago convinces scientists that two large meteorites – hitting the planet millions of years apart – triggered a pair of mega-tsunamis. These gigantic waves, likely 120 metres high, forever scarred the Martian landscape and yielded evidence of cold, salty oceans.
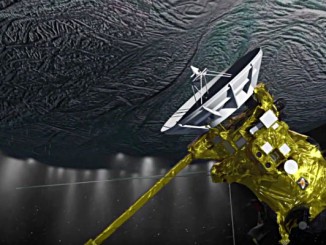
Cassini ready to dive deep into Saturn moon’s erupting water plume
On Wednesday, 28 October 2015, NASA’s Cassini spacecraft will take the deepest dive ever through the plume of ice, water vapour and organic molecules spraying from the south polar region of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. Scientists hope this close flyby will shed light on what’s happening beneath the moon’s icy surface. With a global ocean and likely hydrothermal activity, could Enceladus have the ingredients needed to support simple forms of life?
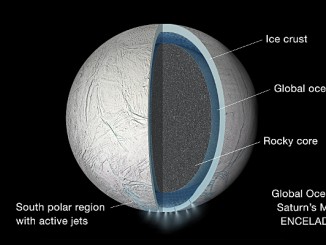
Cassini finds global ocean under icy crust of Saturn’s moon Enceladus
A global ocean lies beneath the icy crust of Saturn’s geologically active moon Enceladus, according to new research using data from NASA’s Cassini mission. Researchers found the magnitude of the moon’s very slight wobble, as it orbits Saturn, can only be accounted for if its outer ice shell is not frozen solid to its interior, meaning a global ocean must be present.


