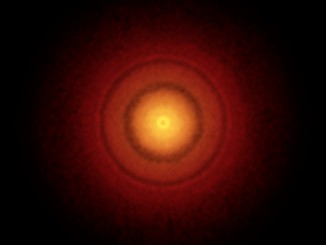
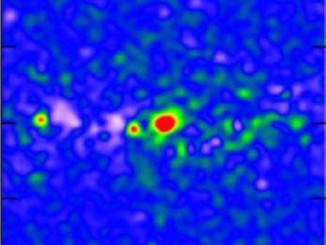
Understanding stellar adolescence through T-Tauri stars
A newborn star typically goes through four stages of adolescence. It begins life as a protostar, accreting material and developing a proto-planetary disc. Slowly, stellar winds and radiation blow away the surrounding shell of gas and dust. Next, when the surrounding envelope has cleared, is called the T-Tauri phase. Finally, accretion stops and the source’s radiation comes from the star’s photosphere.