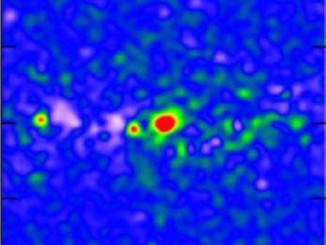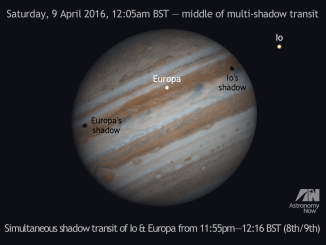
Jupiter continues to delight and amaze observers during April
The impact of a small comet or asteroid on Jupiter observed by European amateur astronomers on 17 March has heightened interest in the solar system’s largest planet. While such an event is uncommon, Jupiter and its family of four bright Galilean moons provide a wealth of other interesting phenomena to view with small telescopes during April.