
Andromeda

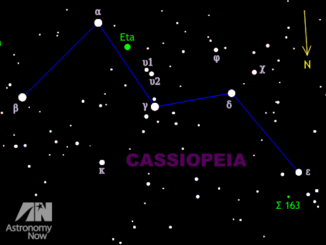
Hunting for colourful double and triple stars in the constellation of Cassiopeia
The instantly recognisable five-star M-shaped pattern of stars representing the constellation Cassiopeia (pronounced kas-ee-uh-pee-uh) lies almost overhead in the early evening as seen from the British Isles over the festive period. Cassiopeia is rich in wonderful double and multiple stars, so here’s our guide to some of the best for typical backyard telescopes.

Seeing double in the autumn sky
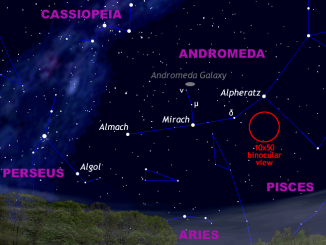
Now that the season of mists and mellow fruitfulness is upon us and the bright summer stars and planets are slipping away to the west, why not seek out some of the spectacular double stars of the autumn sky? We show you how to find some celestial gems suitable for small to medium telescopes in the constellations of Aquarius, Aries and Andromeda.

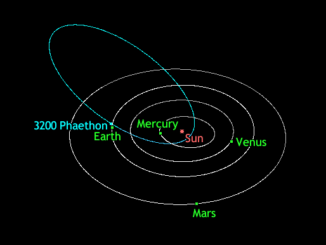
See asteroid Phaethon, source of the Geminids, in a close brush with Earth
As shooting-star devotees prepare for the naked-eye spectacle of the Geminid meteor shower in mid-December, owners of small telescopes can also witness the close passage of the meteors’ parent body — a curious “rock comet” known as 3200 Phaethon, galloping through the constellations of Auriga, Perseus, Andromeda, Pisces and Pegasus at a rate of up to 15 degrees/day.

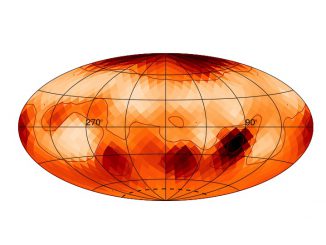
‘Starspot’ images of nearby star give insights into early Sun
Astronomers have used interferometry to create a time-lapse of the nearby star zeta Andromedae over one of its 18-day rotations that show starspots — sunspots outside our solar system. The pattern of spots on the star is very different from their typical arrangement on our Sun, challenging current theories of how stars’ magnetic fields influence their evolution.
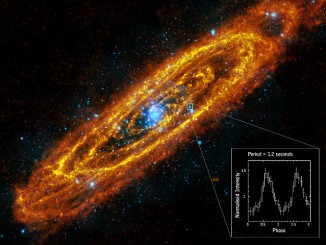
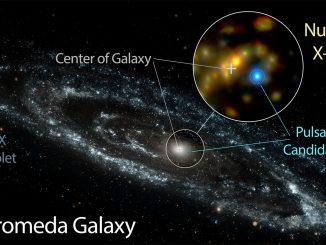
Andromeda Galaxy’s first spinning neutron star found
Decades of searching in the Andromeda Galaxy has finally paid off, with the discovery of an elusive breed of stellar corpse — a neutron star, by ESA’s XMM-Newton space telescope. Neutron stars are the small and extraordinarily dense remains of a once-massive star that exploded as a powerful supernova at the end of its natural life.
