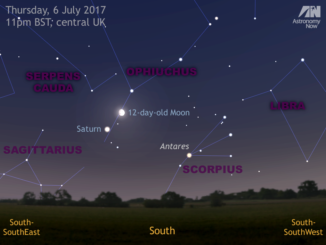
See asteroid Florence’s close dolphin encounter on 2—3 September
During the first week of September, observers have an opportunity to see a bright near-Earth asteroid known as 3122 Florence (aka 1981 ET3) as it sails by our planet. On the night of 2—3 September, observers in the UK and Western Europe can see this 4.4 kilometre-wide space rock pass through a prominent asterism in the constellation of Delphinus, the dolphin.