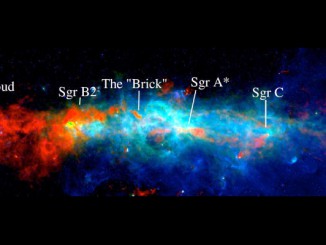
Mysterious flaring X-ray objects discovered in nearby galaxies
Astronomers have found a pair of extraordinary cosmic objects that dramatically burst in X-rays, flaring up to become about a hundred times brighter in less than a minute, before returning to original X-ray levels after about an hour. This discovery may represent a new class of explosive events found in space.