
Asteroids


Asteroids identified as source of Moon’s water
According to a new international study, most (>80 percent) of the water inside the Moon was delivered by asteroids similar to carbonaceous chondritic meteorites during the early lunar evolution, approximately 4.5—4.3 billion years ago. A similar delivery of water to the Earth would have been occurring within this same interval of time.

2007 OR10: the largest unnamed world in the solar system
By combining data from two space observatories, astronomers have revealed something surprising: a 955-mile-wide dwarf planet named 2007 OR10 is significantly larger than previously thought. Although its 547-year-long elliptical orbit brings it nearly as close to the Sun as Neptune, 2007 OR10 is currently twice as far from the Sun as Pluto.
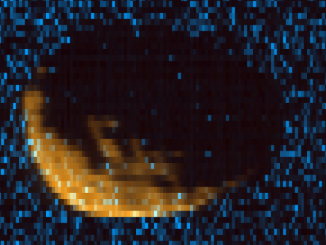
Solving the mystery of how Mars’ moon Phobos formed
In late November and early December 2015, NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission made a series of close approaches to the Martian moon Phobos. Among the data returned were spectral images of Phobos in the ultraviolet. The images will allow MAVEN scientists to better assess the composition of this enigmatic object, whose origin is unknown.

Asteroids found to be the Moon’s main ‘water supply’
Water reserves found on the Moon are the result of asteroids acting as “delivery vehicles” and not of falling comets as was previously thought. Using computer simulation, scientists from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology and the RAS Geosphere Dynamics Institute have discovered that a large asteroid can deliver more water to the lunar surface than the cumulative fall of comets over a billion year period.
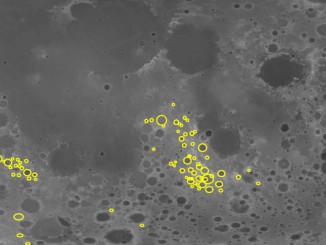
Early Moon’s far-side crust shattered by barrage of small asteroids
Scientists at MIT and elsewhere have identified regions on the far side of the Moon, called the lunar highlands, that may have been so heavily pelted by small asteroids during a period called the Late Heavy Bombardment 4 billion years ago that the impacts completely shattered the upper crust, leaving these regions essentially as fractured and porous as they could be.




