
Alan Stern


New Horizons’ next target might be a binary pair
Ground observations of the New Horizons spacecraft’s next target last month revealed the distant object, lurking in the outer Solar System more than four billion miles from Earth, might have an unconventional elongated shape, or even consist of two icy bodies orbiting one another in an age-old cosmic dance.

New Horizons to continue mission of discovery with Kuiper Belt encounter
Scientists planning the the next phase of NASA’s New Horizons mission, a robotic craft that completed the first exploration of Pluto in 2015, are going into the flyby of a frozen, faraway city-sized clump of rock on New Year’s Day 2019 armed with little knowledge of the target lurking around 4 billion miles from Earth.

New Horizons’ best close-up of Pluto’s surface
A mosaic strip just released by the New Horizons team now includes all of the highest-resolution images taken by the NASA probe. The mosaic affords scientists and the public the best opportunity to examine the fine details of the various types of terrain on Pluto, and determine the processes that formed and shaped them.

Pluto’s interactions with the solar wind are unique
Using data gathered by NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft on its Pluto flyby in July 2015, the dwarf planet has some characteristics less like that of a comet and more like much larger planets, according to the first analysis of Pluto’s unique interaction with the solar wind — the charged particles that spew off from the Sun into the solar system at a supersonic 1 million mph.
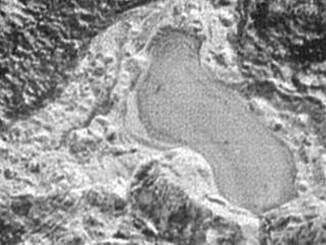
A pond of frozen nitrogen on Pluto
This feature appears to be a frozen, former lake of liquid nitrogen, located in a mountain range just north of Pluto’s informally named Sputnik Planum. Captured by the New Horizons’ Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) as the spacecraft flew past Pluto on 14 July 2015, the image shows the possible lake to be about 20 miles (30 kilometres) across.


No. 1 New Horizons at Pluto
The long-awaited fly-by of Pluto by the New Horizons spacecraft, on 14 July 2015, was an event 85 years in the making, following Pluto’s discovery by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930. Since then, Pluto has gone from planet to dwarf planet, but despite protestations from the New Horizons team, its reclassification never really changed the mission or the importance of what it would find at Pluto.
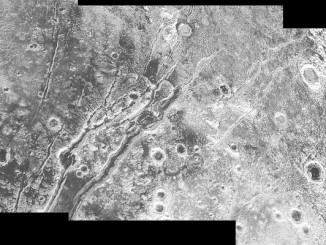
New findings on Pluto and its moons from New Horizons
Five months after NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft flew past Pluto, knowledge about this distant system continues to unfold, yet the spacecraft is less than halfway through transmitting data about the Pluto system to Earth. New Horizons science team members presented the latest findings at the American Geophysical Union (AGU) autumn meeting in San Francisco.

New Horizons returns first, best images of Pluto
It is almost five months since New Horizons’ epic encounter with Pluto, but the captured images and data will stream back to Earth across 3 billion miles of interplanetary space for a further 11 months. The first in a series of the best close-ups of the dwarf planet that humans may see for decades have been released, obtained when the spacecraft was just 15 minutes before closest approach during the 14 July flyby.
