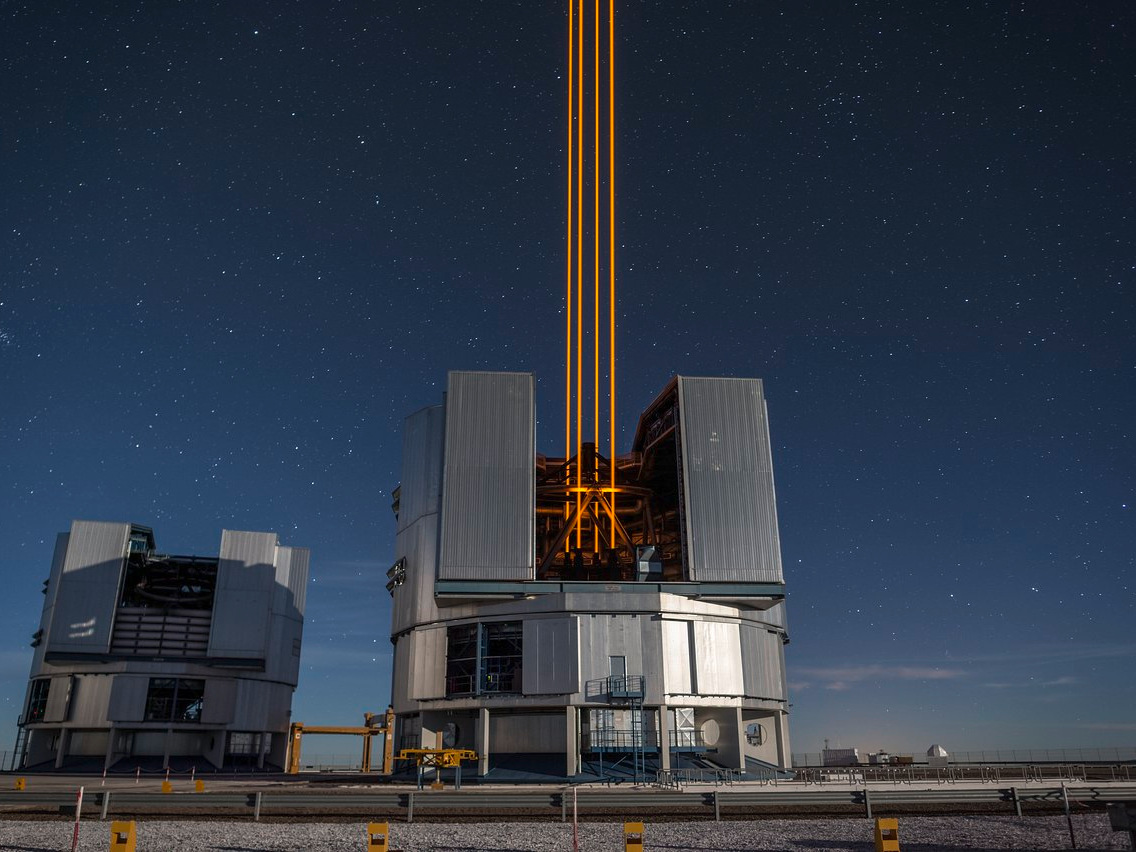
ESO staff were present for the event, along with senior representatives of the companies that have manufactured the different components of the new system.

The Four Laser Guide Star Facility is an example of how ESO enables European industry to lead complex research and development projects. The fibre laser used by the 4LGSF is also one of the most successful transfers of ESO technology to industry.
TOPTICA, the German main contractor, was responsible for the laser system and provided the oscillator, the frequency doubler, and the system control software. Wilhelm Kaenders, president of TOPTICA, said: “TOPTICA has enjoyed the collaboration with ESO tremendously. It is not only the personal thrill of being engaged with astronomy, an old passion, again, and working with very clever ESO technologists; it is also the inspiration that we have received for our own commercial product development.”
MPBC of Canada provided the fibre laser pumps and Raman amplifiers, which are based on an ESO licensed patent. Jane Bachynski, President of MPB Communications Inc., said: “MPBC is proud to have worked with ESO in the development of Raman fibre amplifiers to much higher powers, allowing MPBC to bring this technology to the stars. This event marks the culmination of many years of hard work on behalf of all involved.”
TNO in the Netherlands manufactured the optical tube assemblies, which expand the laser beams and direct them into the sky. Paul de Krom, CEO of TNO, said: “TNO valued the cooperative working environment during the development of the optical tube assemblies and looks forward to the opportunity to work with ESO and the other partners in the 4LGSF project in the future.”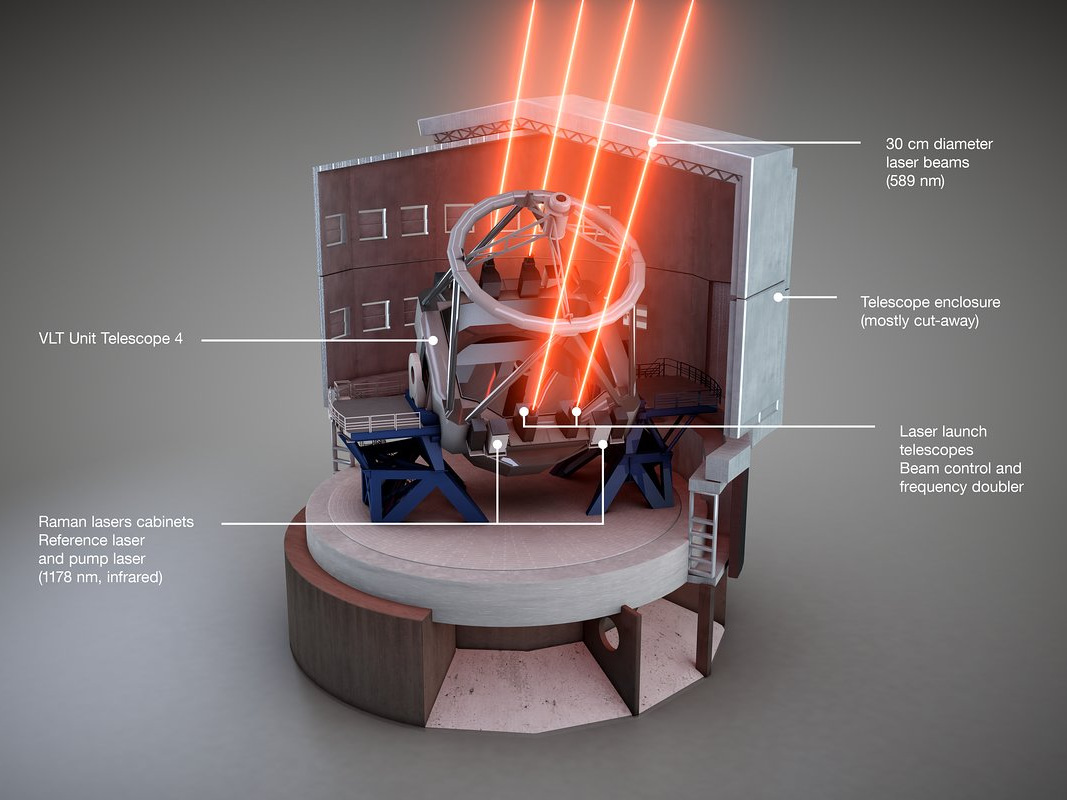
The 4LGSF lasers were developed by ESO with industry and have already been procured, among others, by the Keck Observatory (which contributed to the industrial laser development cost along with the European Commission) and the Subaru Telescope. In the future these industrial lasers will also feature on the telescopes at the Gemini Observatory and will be the preferred choice for several other observatories and extremely large telescope projects.
The new techniques developed for the Four Laser Guide Star Facility pave the way for the adaptive optics system of the European Extremely Large Telescope (E-ELT), the world’s biggest eye on the sky.