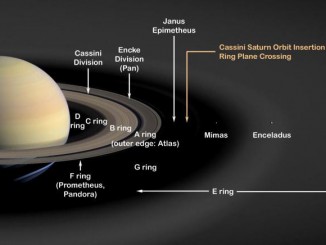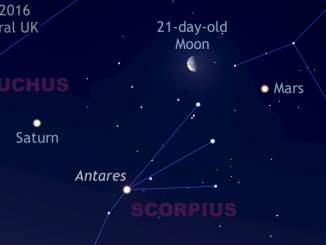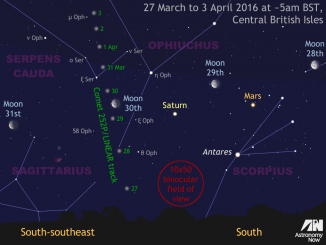
See comet 252P emerge in the UK predawn sky
When 252P/LINEAR passed just 14 lunar distances from Earth on 21 March, the comet was galloping across the far southern sky at a rate of almost ten degrees per day. Now rapidly heading north, 252P finally appears in the predawn UK sky. While moonlight will interfere with current observations, the comet is much brighter than predicted.