
Month: September 2016


See the Moon meet Saturn and Mars in the evening sky
A hundred days have passed since Mars was closest to Earth this year, but the Red Planet can still be seen in the early evening sky close to the jewel of the solar system, Saturn. If you wish to identify this pair of planets, then a convenient celestial marker in the form of the waxing crescent Moon passes by on the evenings of 8—9 September in the UK and Western Europe.

New research reveals hundreds of undiscovered black holes
It is only as recently as 2013 that astrophysicists found individual black holes in globular clusters via rare phenomena in which a companion star donates material to the black hole. New research by the University of Surrey on a globular cluster known as NGC 6101 shows that it could host several hundred black holes — a phenomenon that until recently was thought impossible.

Rare fossil relic of early Milky Way discovered
A fossilised remnant of the early Milky Way harbouring stars of hugely different ages has been revealed by an international team of astronomers. Terzan 5 resembles a globular cluster, but is unlike any other cluster known. It contains stars remarkably similar to the most ancient stars in the Milky Way and bridges the gap in understanding between our galaxy’s past and its present.

Brown dwarfs hiding in plain sight in our solar neighbourhood
Brown dwarfs are sometimes called failed stars as they are too small to sustain the hydrogen fusion process that powers stars. Their temperatures can range from nearly as hot as a star to as cool as a planet and their masses also range between star-like and giant-planet-like. A near-infrared survey has discovered several ultracool brown dwarfs in the Sun’s vicinity.

Earth’s carbon came from ancient collision with Mercury-like planet
How did carbon-based life develop on Earth, given that most of the planet’s carbon should have either boiled away in the planet’s earliest days or become locked in Earth’s core? A new study suggests all of the planet’s life-giving carbon came from a collision with an embryonic planet similar to Mercury approximately 4.4 billion years ago.
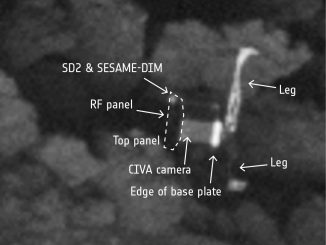
Philae found! Rosetta’s lander wedged in cometary crevice
Less than a month before the end of the mission, Rosetta’s high-resolution camera has revealed the Philae lander wedged into a dark crack on Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. The images were taken on 2 September by the OSIRIS narrow-angle camera as the orbiter came within 2.7 kilometres of the comet’s surface.

Hubble peers into the maelstrom
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows a stellar nursery known as N159 — a maelstrom of glowing gas and dark dust within one of the Milky Way’s satellite galaxies, the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). N159 is located over 160,000 light-years away. It resides just south of the Tarantula Nebula, another massive star-forming complex within the LMC.

The supernova that wasn’t: a tale of three cosmic eruptions
Combining images taken with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope over more than 20 years, a team of researchers has discovered that Eta Carinae, a very massive star system that has puzzled astronomers since it erupted in a supernova-like event in the mid-19th century, has a past that’s much more violent than they thought.

Orion 60mm multi-use guidescope
These days, more is expected of a finder than to merely direct the main telescope to a celestial object of interest. This versatile 60mm f/4 instrument possesses a fine movement non-rotating helical focuser that has been designed to double as a traditional finder or guidescope with Orion’s StarShoot AutoGuiders, says reviewer Steve Ringwood.
