
Caltech



LIGO resumes search for gravitational waves
After a series of upgrades, the twin detectors of LIGO, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory, have turned back on and resumed their search for ripples in the fabric of space and time known as gravitational waves. Now boasting a 25 percent improvement in sensitivity, LIGO recommenced science observations at 4pm GMT on 30 November.
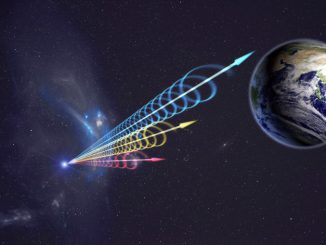
Mapping the cosmic web with fast radio bursts
Fast radio bursts, or FRBs, are mysterious flashes of radio waves originating outside our Milky Way galaxy. A team of scientists, jointly led by Caltech postdoctoral scholar Vikram Ravi and Curtin University research fellow Ryan Shannon, has now observed the most luminous FRB to date, called FRB 150807.


Curious tilt of the Sun traced to undiscovered Planet Nine
Planet Nine — the undiscovered planet at the edge of the solar system that was predicted by the work of Caltech’s Konstantin Batygin and Mike Brown in January 2016 — appears to be responsible for the unusual tilt of the Sun. The large and distant planet may be adding a wobble to the solar system, giving the appearance that the Sun is tilted slightly.

Milky Way’s most-mysterious star is even stranger than astronomers thought
A star known as KIC 8462852 in the constellation Cygnus has been raising eyebrows both in and outside of the scientific community for the past year. In 2015 a team of astronomers announced that the star underwent a series of very brief, non-periodic dimming events while being monitored by NASA’s Kepler space telescope. A new study has deepened the mystery.

Pirouetting Pleiads provide clues to stellar structure and evolution
Like cosmic ballet dancers, the stars of the Pleiades cluster are spinning, but all at different speeds. By watching these stellar dancers, NASA’s Kepler space telescope has helped amass the most complete catalogue of rotation periods for stars in a cluster. This information can provide insight into where and how planets form around these stars, and how such stars evolve.

Keck Observatory measures oxygen in galaxy 12 billion years ago
Astronomers have made the first accurate measurement of the abundance of oxygen in a distant galaxy. Oxygen is created inside stars and released into interstellar gas when stars die. Quantifying the amount of oxygen, the third-most abundant chemical element in the universe, is key to understanding how matter cycles in and out of galaxies.

Chorus of black holes sings in X-rays
Supermassive black holes do not give off any of their own light, hence the word “black” in their name. However, many black holes pull in surrounding material and emit powerful bursts of X-rays. Collectively, these active black holes can be thought of a cosmic choir, singing in the language of X-rays. Their “song” is what astronomers call the cosmic X-ray background.
