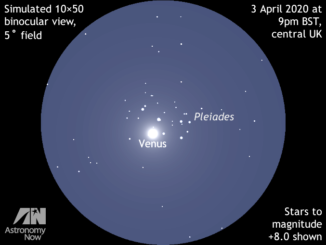
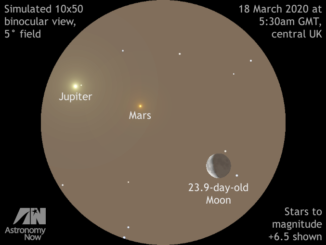
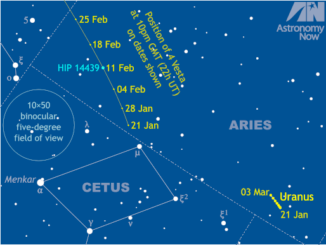
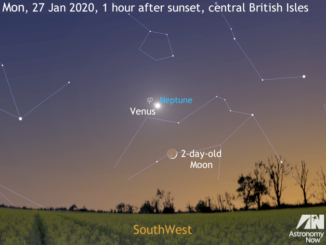
Get ready for Comet ATLAS (C/2019 Y4) in the northern spring sky!
Comet C/2019 Y4 was discovered by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) on 28 December last year and brightened 6000-fold in just two months to attain magnitude +7.5 on 1 April. Alas, the comet’s nucleus has now fragmented, dashing hopes for a conspicuous naked-eye spectacle in the constellation of Perseus. Here’s our telescopic observing guide.