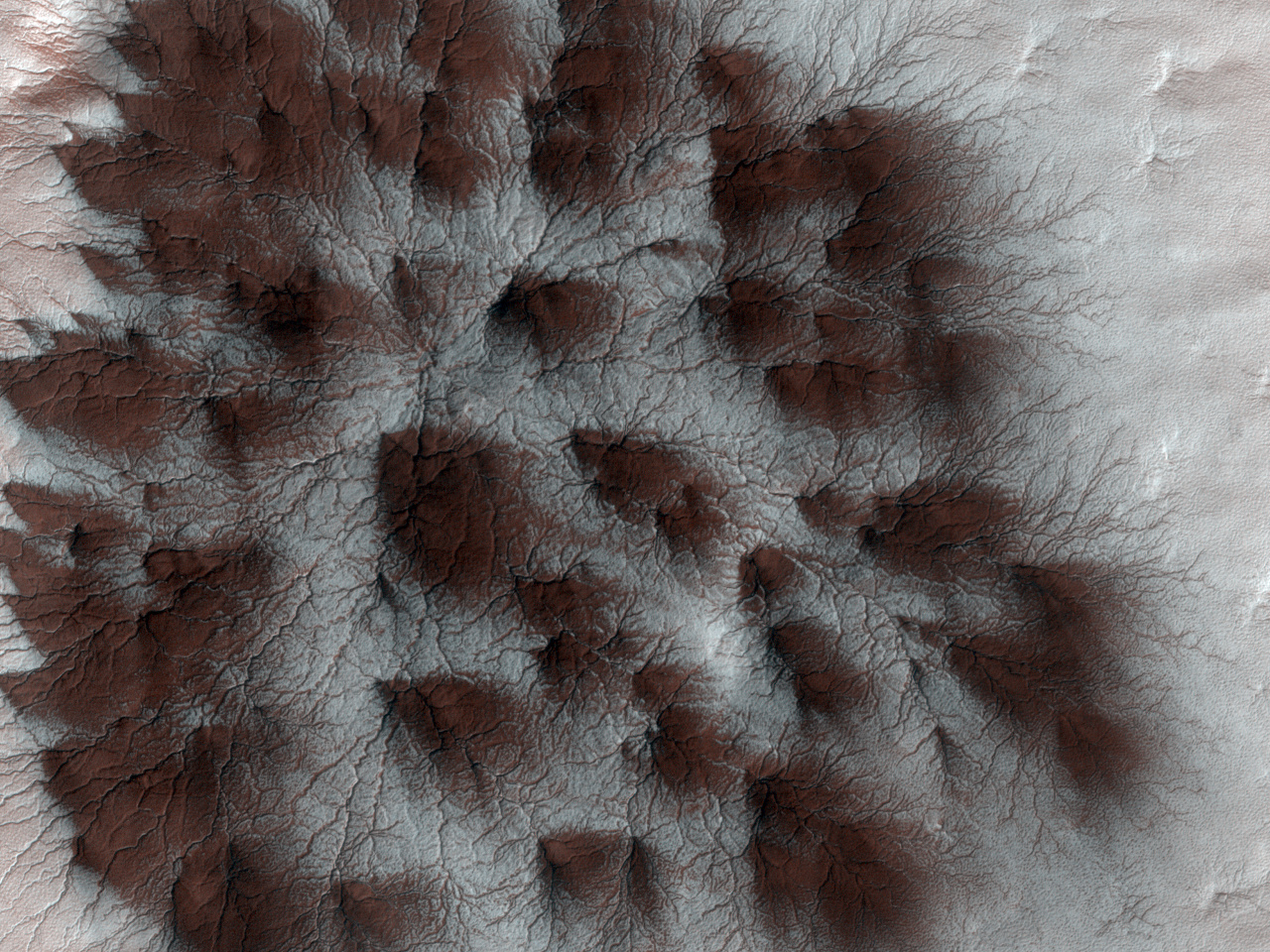
Mars’ seasonal cap of carbon dioxide ice has eroded many beautiful terrains as it sublimates (goes directly from ice to vapour) every spring. In the region where the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter took this image, we see troughs that form a starburst pattern. In other areas these radial troughs have been referred to as spiders, simply because of their shape. In this region the pattern looks more dendritic as channels branch out numerous times as they get further from the centre.
Mars’ seasonal cap of carbon dioxide ice has eroded many beautiful terrains as it sublimates (goes directly from ice to vapour) every spring. In the region where the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter took this image, we see troughs that form a starburst pattern. In other areas these radial troughs have been referred to as spiders, simply because of their shape. In this region the pattern looks more dendritic as channels branch out numerous times as they get further from the centre.
The troughs are believed to be formed by gas flowing beneath the seasonal ice to openings where the gas escapes, carrying along dust from the surface below. The dust falls to the surface of the ice in fan-shaped deposits.
This image, covering an area about 1 kilometre (0.6 mile) across, is a portion of the HiRISE observation catalogued as ESP_011842_0980, taken on 4 February 2009. The observation is centered at 81.8° south latitude, 76.2° east longitude. The image was taken at a local Mars time of 4:56pm and the scene is illuminated from the west with a solar incidence angle of 78°, thus the Sun was about 12° above the horizon. At a solar longitude of 203.6°, the season on Mars is northern autumn.