“Most of the known planets are hundreds of light-years away. This one is practically a next-door neighbour,” said astronomer Lars A. Buchhave of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA).
“Its proximity makes HD 219134 ideal for future studies. The James Webb Space Telescope and future large ground-based observatories are sure to point at it and examine it in detail,” said lead author Fatemeh (Ati) Motalebi of the Geneva Observatory.
The newfound world, designated HD 219134b, was discovered using the HARPS-North instrument on the 3.6-metre Telescopio Nazionale Galileo in the Canary Islands. The CfA is a major partner with the Geneva Observatory on the HARPS-North Collaboration, which includes several other European partners.
HARPS-North detects planets using the radial velocity method, which allows astronomers to measure a planet’s mass. HD 219134b weighs 4.5 times the mass of Earth, making it a super-Earth.
With such a close orbit, researchers realised that there was good possibility the planet would transit its star. In April of this year they targeted the system with NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope. At the appropriate time, the star dimmed slightly as the planet crossed the star’s face. Measuring the depth of the transit gave the planet’s size, which is 1.6 times Earth. As a result, the team can calculate the planet’s density, which works out to about 6 g/cm3. This shows that HD 219134b is a rocky world.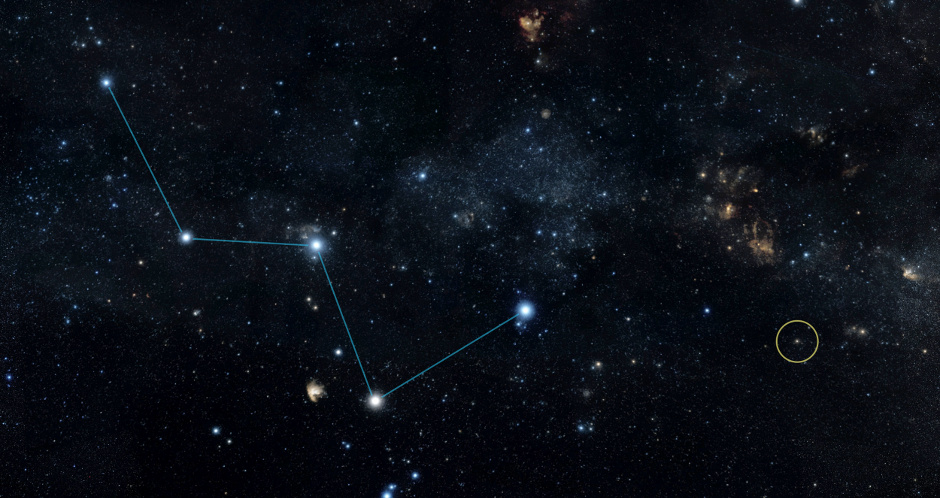
HD 219134 is an orange Type K star somewhat cooler, smaller and less massive than our Sun. Its key measurements have been pinned down very precisely, which thus allows a more precise determination of the properties of its accompanying planets.
This discovery came from the HARPS-North Rocky Planet Search, a dedicated survey examining about 50 nearby stars for signs of small planets. The team targeted nearby stars because those stars are brighter, which makes follow-up studies easier. In particular, additional observations might allow the detection and analysis of planetary atmospheres.
HD 219134 was one of the closest stars in the sample, so it was particularly lucky to find that it hosts a transiting planet. This system now holds the record for the nearest transiting exoplanet. As such, it likely will be a favorite for researchers for years to come.