NASA’s Fermi finds hints of gamma-ray cycle in active galaxy
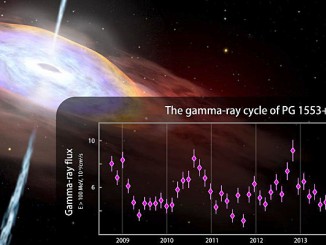
Astronomers using data from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope have detected hints of periodic changes in the brightness of a so-called “active” galaxy, whose emissions are powered by a supersized black hole. If confirmed, the discovery would mark the first years-long cyclic gamma-ray emission ever detected from any galaxy, which could provide new insights into physical processes near the black hole.