
European Space Agency




European Rosetta spacecraft poised for comet crash landing
The European Space Agency’s Rosetta spacecraft closed in Thursday for a deliberate crash landing on the surface of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko on Friday, a slow-motion kamikaze plunge to bring the enormously successful mission to an end after more than two years of unprecedented close-range observations.

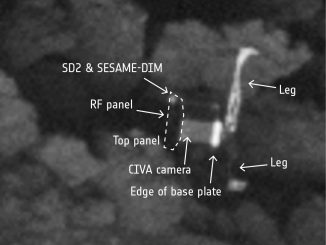
Philae found! Rosetta’s lander wedged in cometary crevice
Less than a month before the end of the mission, Rosetta’s high-resolution camera has revealed the Philae lander wedged into a dark crack on Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. The images were taken on 2 September by the OSIRIS narrow-angle camera as the orbiter came within 2.7 kilometres of the comet’s surface.
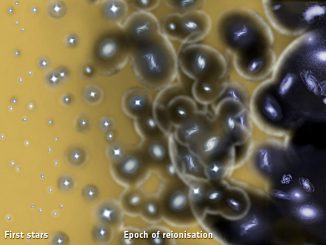
First stars formed even later than previously thought
ESA’s Planck satellite has revealed that the first stars in the universe started forming later than previous observations of the Cosmic Microwave Background indicated. This new analysis also shows that these stars were the only sources needed to account for reionising atoms in the cosmos, having completed half of this process when the universe had reached an age of 700 million years.

Hubble’s fireball
In this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image we see the central Wolf-Rayet star known as Hen 2-427 — more commonly known as WR 124 — surrounded by the nebula M1-67. Both objects are found in the constellation of Sagitta some 15,000 light-years away. The hot clumps of gas ejected by the star into space are travelling at over 150,000 kilometres per hour.

ExoMars orbiter fine-tunes path toward red planet
A European spacecraft cruising toward Mars fired its main engine, tweaking its trajectory and helping set up for carefully-choreographed simultaneous maneuvers to place part of the tandem mission into orbit around the red planet and deposit a stationary battery-powered lander on the Martian surface.

