Star Epsilon (ε) Tauri plays hide and seek with the crescent Moon on 29 March
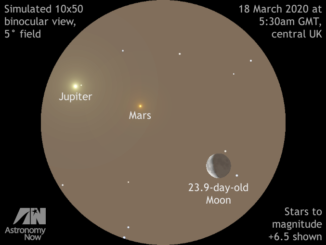
On Sunday, 29 March around civil dusk, observers throughout the British Isles with suitably steadied binoculars and small telescopes can watch naked-eye star Epsilon (ε) Tauri disappear behind the darkened hemisphere of the almost 5-day-old waxing crescent Moon, reappearing again slightly more than an hour later. Here’s our where and when guide to viewing it.