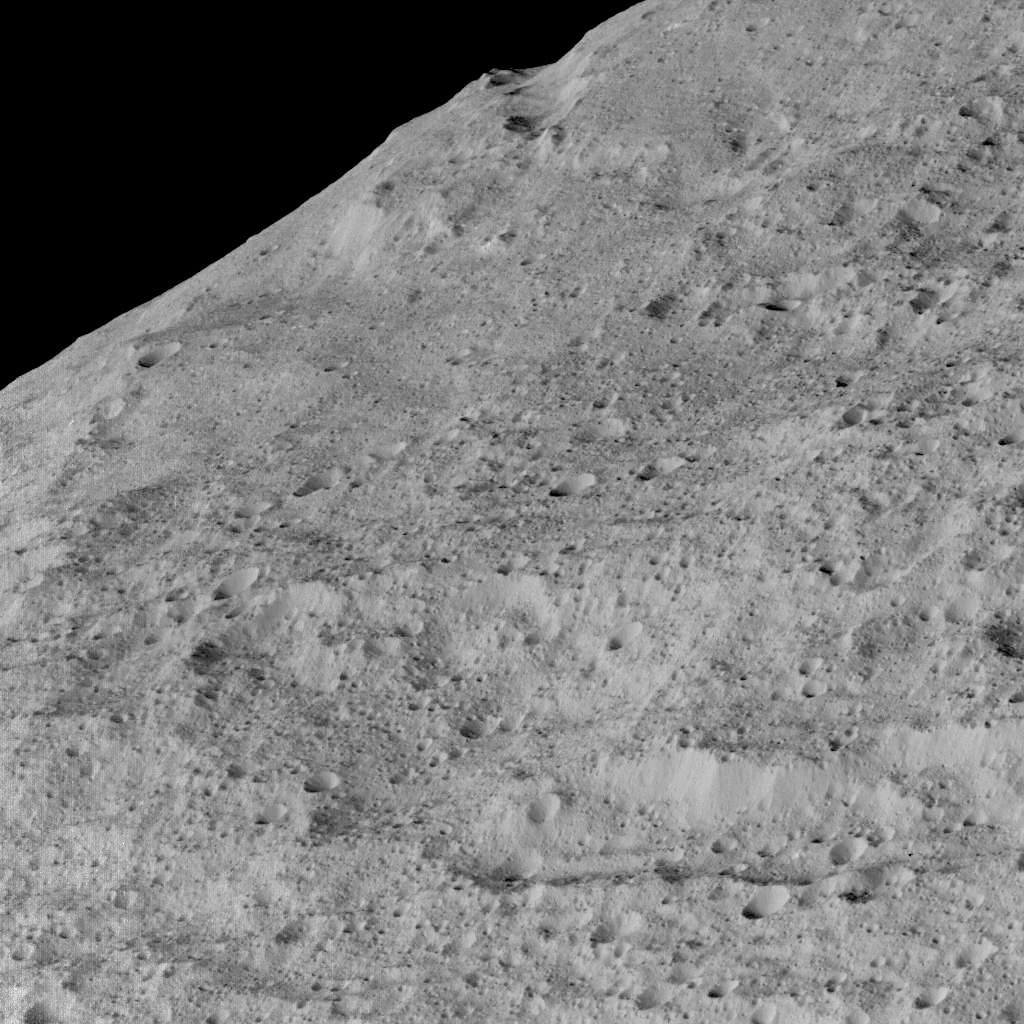
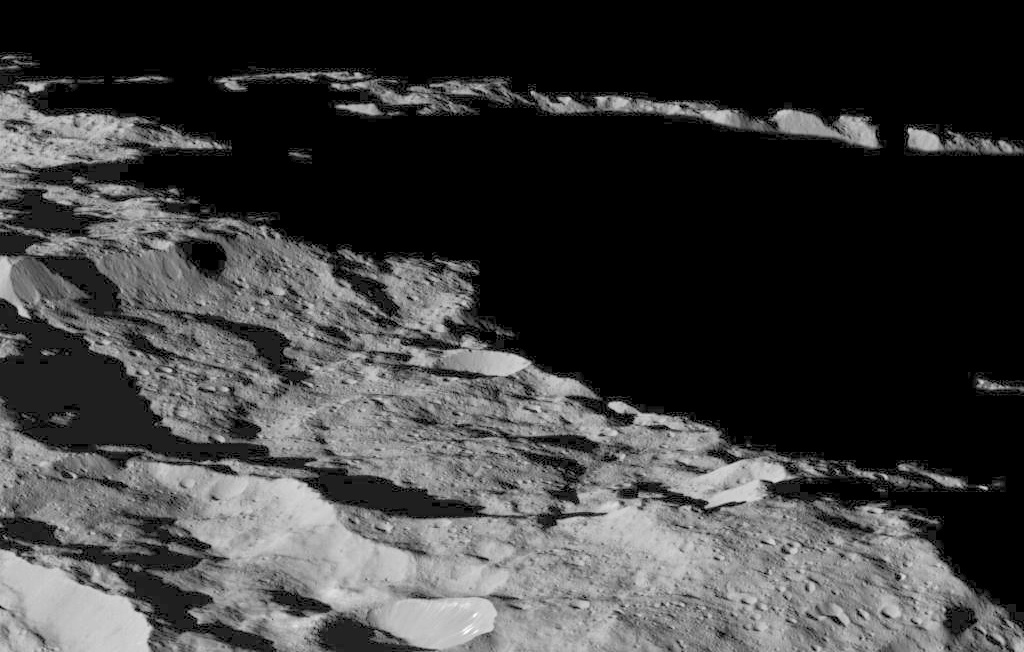
Dawn took these images of the southern hemisphere of Ceres on 10 December, at an approximate altitude of 240 miles (385 kilometres), which is its lowest-ever orbital altitude. Dawn will remain at this altitude for the rest of its mission, and indefinitely afterward. The resolution of the new images is about 120 feet (35 metres) per pixel.
Among the striking views is a chain of craters called Gerber Catena, located just west of the large crater Urvara. Troughs are common on larger planetary bodies, caused by contraction, impact stresses and the loading of the crust by large mountains — Olympus Mons on Mars is one example. The fracturing found all across Ceres’ surface indicates that similar processes may have occurred there, despite its smaller size (the average diameter of Ceres is 584 miles, or 940 kilometres). Many of the troughs and grooves on Ceres were likely formed as a result of impacts, but some appear to be tectonic, reflecting internal stresses that broke the crust.
The images were taken as part of a test of Dawn’s backup framing camera. The primary framing camera, which is essentially identical, began its imaging campaign at this lowest orbit on 16 December. Both cameras are healthy.
Dawn’s other instruments also began their intense period of observations this month. The visible and infrared mapping spectrometer will help identify minerals by looking at how various wavelengths of light are reflected by the surface of Ceres. The gamma ray and neutron detector is also active. By measuring the energies and numbers of gamma rays and neutrons, two components of nuclear radiation, it will help scientists determine the abundances of some elements on Ceres.
“As we take the highest-resolution data ever from Ceres, we will continue to examine our hypotheses and uncover even more surprises about this mysterious world,” said Chris Russell, principal investigator of the Dawn mission, based at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Dawn is the first mission to visit a dwarf planet, and the first mission outside the Earth-Moon system to orbit two distinct solar system targets. It orbited protoplanet Vesta for 14 months in 2011 and 2012, and arrived at Ceres on 6 March 2015.