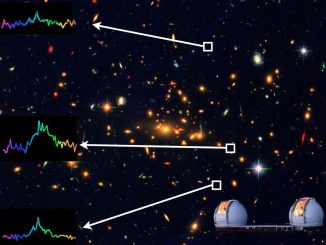
Breakthrough Listen searches new-found nearby planet Proxima b for signs of ET
Breakthrough Listen, the 10-year, $100-million astronomical search for intelligent life beyond Earth launched in 2015 by Internet entrepreneur Yuri Milner and Stephen Hawking, has just announced its first observations of newly-discovered Earth-size planet Proxima b orbiting the nearest star to the Sun using the Parkes Radio Telescope in New South Wales, Australia.