Detection of methanol shows comets are forming in distant solar system
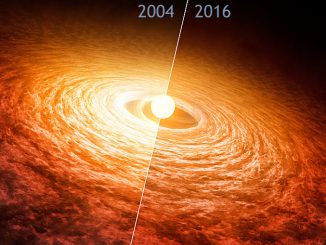
Astronomers have found the organic molecule methyl alcohol, or methanol, in the protoplanetary disc of TW Hydrae, 175 light-years from Earth — the first such detection of this chemical compound in a young planet-forming disc. Since methanol forms on the icy coatings of dust grains, this discovery provides a window into the region where comets are likely forming.