The Georgia Tech simulations investigate the possibility that these red giants were dimmed after they were stripped of tens of percent of their mass millions of years ago during repeated collisions with an accretion disc at the galactic centre. The very existence of the young stars, seen in astronomical observations today, is an indication that such a gaseous accretion disc was present in the galactic centre because the young stars are thought to have formed from it as recently as a few million years ago.
The study is published in the June edition of The Astrophysical Journal. It is the first to run computer simulations on the theory, which was introduced in 2014.
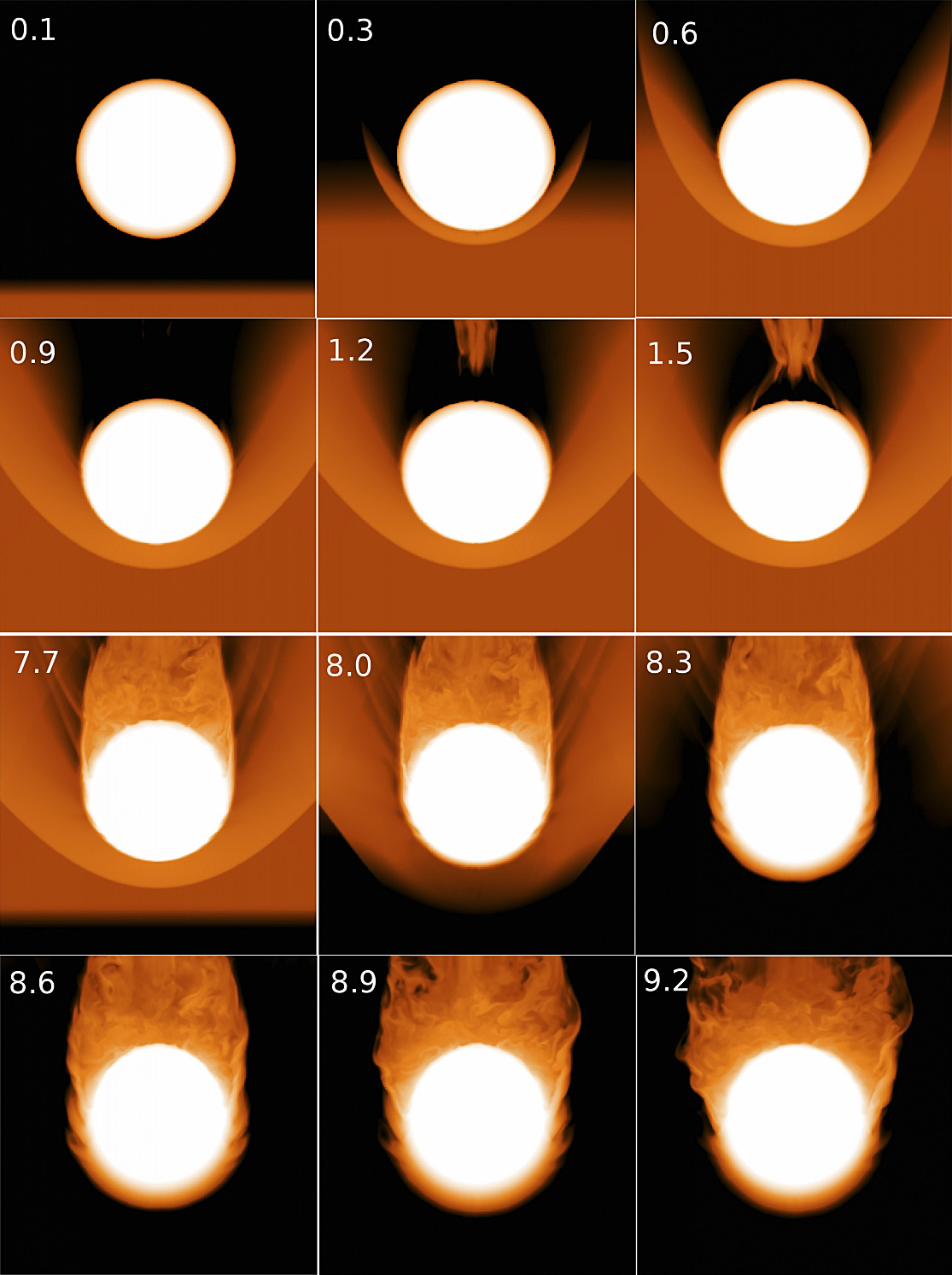
Astrophysicists in Georgia Tech’s College of Sciences created models of red giants similar to those that are supposedly missing from the galactic centre — stars that are more than a billion years old and tens of times larger in size than the Sun. They put them through a computerised version of a wind tunnel to simulate collisions with the gaseous disc that once occupied much of the space within 0.5 parsecs of the galactic centre. They varied orbital velocities and the disc’s density to find the conditions required to cause significant damage to the red giant stars.
“Red giants could have lost a significant portion of their mass only if the disc was very massive and dense,” said Tamara Bogdanovic, the Georgia Tech assistant professor who co-led the study. “So dense, that gravity would have already fragmented the disc on its own, helping to form massive clumps that became the building blocks of a new generation of stars.”
The simulations suggest that each of the red giant stars orbited its way into and through the disc as many as dozens of times, sometimes taking as long as days to weeks to complete a single pass-through. Mass was stripped away with each collision as the star blistered the fragmenting disc’s surface.
According to former Georgia Tech undergraduate student Thomas Forrest Kieffer, the first author on the paper, it’s a process that would have taken place 4 to 8 million years ago, which is the same age as the young stars seen in the centre of the Milky Way today.
“The only way for this scenario to take place within that relatively short time frame,” Kieffer said, “was if, back then, the disc that fragmented had a much larger mass than all the young stars that eventually formed from it — at least 100 to 1,000 times more mass.”
“We don’t know very much about the conditions that led to the most recent episode of star formation in the galactic centre or whether this region of the galaxy could have contained so much gas,” Bogdanovic said. “If it did, we expect that it would presently house under-luminous red giants with smaller orbits, spinning more rapidly than expected. If such population of red giants is observed, among a small number that are still above the detection threshold, it would provide direct support for the star-disc collision hypothesis and allow us to learn more about the origins of the Milky Way.”



