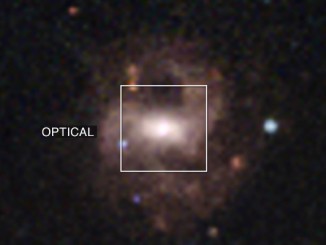
Some 290 million years ago, a star much like the sun wandered too close to the central black hole of its galaxy. Intense tides tore the star apart, which produced an eruption of optical, ultraviolet and X-ray light that first reached Earth in 2014. Now, a team of scientists using observations from NASA’s Swift satellite have mapped out how and where these different wavelengths were produced in the event, named ASASSN-14li, as the shattered star’s debris circled the black hole.
“We discovered brightness changes in X-rays that occurred about a month after similar changes were observed in visible and UV light,” said Dheeraj Pasham, an astrophysicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and the lead researcher of the study. “We think this means the optical and UV emission arose far from the black hole, where elliptical streams of orbiting matter crashed into each other.”
Astronomers think ASASSN-14li was produced when a sun-like star wandered too close to a 3-million-solar-mass black hole similar to the one at the center of our own galaxy. For comparison, the event horizon of a black hole like this is about 13 times bigger than the sun, and the accretion disk formed by the disrupted star could extend to more than twice Earth’s distance from the sun.
When a star passes too close to a black hole with 10,000 or more times the sun’s mass, tidal forces outstrip the star’s own gravity, converting the star into a stream of debris. Astronomers call this a tidal disruption event. Matter falling toward a black hole collects into a spinning accretion disk, where it becomes compressed and heated before eventually spilling over the black hole’s event horizon, the point beyond which nothing can escape and astronomers cannot observe. Tidal disruption flares carry important information about how this debris initially settles into an accretion disk.
Astronomers know the X-ray emission in these flares arises very close to the black hole. But the location of optical and UV light was unclear, even puzzling. In some of the best-studied events, this emission seems to be located much farther than where the black hole’s tides could shatter the star. Additionally, the gas emitting the light seemed to remain at steady temperatures for much longer than expected.
ASASSN-14li was discovered Nov. 22, 2014, in images obtained by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASASSN), which includes robotic telescopes in Hawaii and Chile. Follow-up observations with Swift’s X-ray and Ultraviolet/Optical telescopes began eight days later and continued every few days for the next nine months. The researchers supplemented later Swift observations with optical data from the Las Cumbres Observatory headquartered in Goleta, California.
In a paper describing the results published March 15 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Pasham, Cenko and their colleagues show how interactions among the infalling debris could create the observed optical and UV emission.
Tidal debris initially falls toward the black hole but overshoots, arcing back out along elliptical orbits and eventually colliding with the incoming stream.
“Returning clumps of debris strike the incoming stream, which results in shock waves that emit visible and ultraviolet light,” said Goddard’s Bradley Cenko, the acting Swift principal investigator and a member of the science team. “As these clumps fall down to the black hole, they also modulate the X-ray emission there.”
Future observations of other tidal disruption events will be needed to further clarify the origin of optical and ultraviolet light.
Goddard manages the Swift mission in collaboration with Pennsylvania State University in University Park, the Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico and Orbital Sciences Corp. in Dulles, Virginia. Other partners include the University of Leicester and Mullard Space Science Laboratory in the United Kingdom, Brera Observatory and the Italian Space Agency in Italy, with additional collaborators in Germany and Japan.