
National Science Foundation

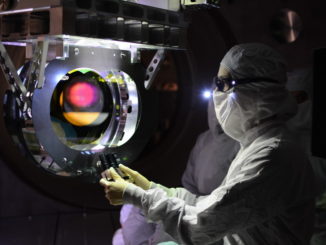
Gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger observed by LIGO and Virgo
The LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo collaboration report the first joint detection of gravitational waves with both the LIGO and Virgo detectors. This is the fourth announced detection of a binary black hole system and the first significant gravitational-wave signal recorded by the Virgo detector, and highlights the scientific potential of a three-detector network of gravitational-wave detectors.



Astronomers investigate distant galaxy’s magnetic field
With the help of a gigantic cosmic lens, astronomers have measured the magnetic field of a galaxy nearly five billion light-years away. The achievement is giving them important new clues about a problem at the frontiers of cosmology — the nature and origin of the magnetic fields that play an important role in how galaxies develop over time.



Are all stars created equal?
Astronomers have found the strongest evidence yet that the formation of massive stars follows a path similar to their lower-mass brethren — but on steroids! The new findings show that the episodic explosive outbursts within what are called accretion discs, known to occur during the formation of average mass stars like our Sun, also happen in the formation of much more massive stars.

Galactic merger exposes supermassive black hole
Astronomers using the super-sharp radio vision of the National Science Foundation’s Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) have found the shredded remains of a galaxy that passed through a larger galaxy, leaving only the smaller galaxy’s nearly-naked supermassive black hole to emerge and speed away at more than 2,000 miles per second.
