
moon

Observing

Observing

Observing

Observing

Observing

News

News

Observing
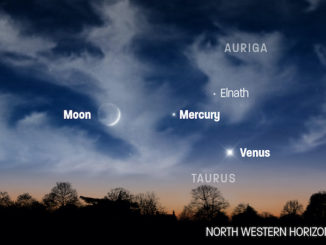
Observing
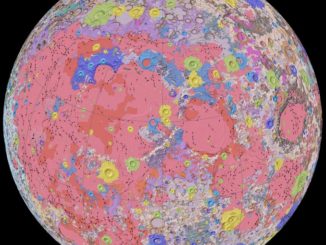
Picture This
