
Magellanic Clouds


Hubble reveals a galaxy fit to burst
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image reveals the vibrant core of the galaxy NGC 3125, approximately 50 million light-years away. Discovered by John Herschel in 1835, NGC 3125 is a great example of a starburst galaxy — a galaxy in which unusually high numbers of new stars are forming, springing to life within intensely hot clouds of gas.
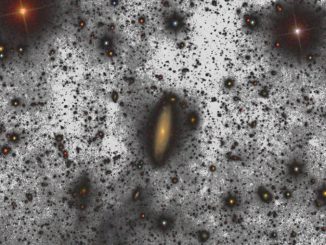
Ten-metre Canary Island telescope obtains deepest Earth-based galaxy image
The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) set out to test the limit of observation which can be reached using the largest optical-infrared telescope in the world: the Gran Telescopio CANARIAS (GTC). The observers managed to obtain an image 10 times deeper than any other obtained from the ground, observing a faint halo of stars around the galaxy UGC0180.

Atacama Pathfinder Experiment (APEX) starts its second decade
The Atacama Pathfinder Experiment (APEX) is a 12-metre radio telescope for observations at submillimetre wavelengths, operating 5,100 metres above sea level in the Atacama Desert. On 25-26 January, the project’s 10th anniversary was celebrated at the APEX base station in Sequitor, San Pedro de Atacama. A number of special guests were present at the occasion.

Zooming into the Coalsack Nebula
Dark smudges almost block out a rich star field in this new image of the Coalsack Nebula captured by the 2.2-metre telescope at ESO’s La Silla Observatory in Chile. This huge, dusky object forms a conspicuous silhouette against the bright, starry band of the Milky Way and has been known to people in the Southern Hemisphere for as long as our species has existed.

Dwarf galaxy WLM becomes star-forming powerhouse
Nearby dwarf galaxy Wolf—Lundmark—Melotte (WLM) poses an intriguing mystery: How is it able to form brilliant star clusters without the dusty, gas-rich environments found in larger galaxies? The answer, astronomers believe, lies in densely packed and previously unrecognised nuggets of star-forming material sprinkled throughout the galaxy.

