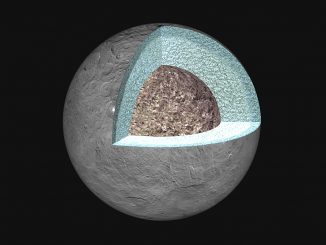
See asteroid 2 Pallas at its best during August 2016
During the Perseid meteor shower, second-largest asteroid 2 Pallas passed close to the southeast of globular cluster Messier 15 in the constellation of Pegasus. The minor planet still lies in the vicinity of this beautiful deep-sky object, reaching opposition on 20 August — here’s our in-depth guide to Pallas at its best.