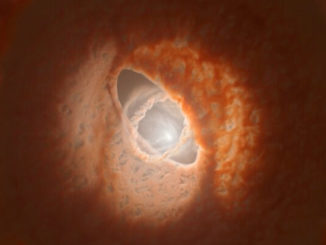
The Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, is the home of spectacular star-forming regions featuring complex tapestries of bright emission nebulae, dark dust lanes and colourful supernova remnants. NGC 2035 is a case in point, a lesser known region of the LMC discovered by the Scottish astronomer James Dunlop in 1826. This view was captured by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope, showing clouds where new stars are being born along with the remnants of a supernova explosion (left).