Professor Mark Sims of Leicester University speaks to Astronomy Now’s Keith Cooper on the discovery that Beagle 2 made it to the surface on Christmas Day 2003.
Related Articles
Observing
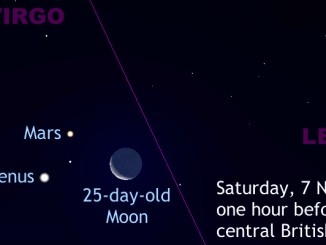
See the Moon join the morning planets on 6-7 November
If you have a clear sky to the southeast an hour before sunrise on the morning of Friday, 6 November you will be greeted by a pairing of the old, waning crescent Moon with largest planet Jupiter. Then, on Saturday, 7 November, a slimmer crescent Moon joins planets Mars and Venus for an even closer triple conjunction. Have your binoculars and cameras ready!
News
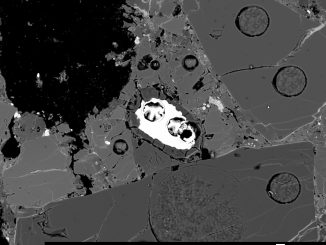
Meteorites delivered water ice to asteroids in early solar system
Planetary scientists have discovered pieces of opal in a meteorite found in Antarctica, a result that demonstrates that meteorites delivered water ice to asteroids early in the history of the solar system. Opal, familiar on Earth as a precious stone used in jewellery, is made up of silica (the major component of sand) with up to 30 percent water in its structure.

