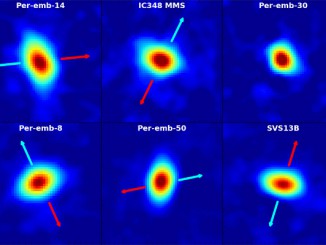
Dust grains could be remnants of stellar explosions billions of years ago
Microscopic particles of stardust, known as “pre-solar grains,” have been found in meteoritic material on Earth. Researchers are investigating whether these particles may have formed in classical novae explosions, ejecting stellar material in the form of gas and dust into the space between stars in the galaxy, eventually to be recycled in the creation of our solar system.