
UC Berkeley


Did a low-mass supernova trigger formation of solar system?
About 4.6 billion years ago, a cloud of gas and dust that eventually formed our solar system was disturbed. The ensuing gravitational collapse formed the proto-Sun with a surrounding disc where the planets were born. Now, forensic evidence from meteorites provides conclusive evidence that a low-mass supernova was the trigger.

Breakthrough Listen to search for intelligent life around weird star
Tabby’s star, otherwise known as KIC 8462852, has provoked so much excitement over the past year, with speculation that it hosts a highly advanced civilisation capable of building orbiting megastructures, that UC Berkeley’s Breakthrough Listen project is devoting hours of time on the Green Bank radio telescope to see if it can detect any extraterrestrial signals.

What happened after the lights came on in the universe?
The National Science Foundation has approved funding to expand the Hydrogen Epoch of Reionisation Array (HERA) in South Africa. Upgrading the number of antennas from 19 to 240 by the year 2018 will enable HERA to study more clearly the impact of cosmic dawn, the moment a few hundred million years after the Big Bang when the first stars and galaxies blazed awake.

Hubble confirms new dark spot on Neptune
New images captured by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) confirm the presence of a dark vortex roughly 3,000 miles (4,800 kilometres) across in the atmosphere of Neptune. Though similar features were seen during the Voyager 2 flyby of Neptune in 1989 and by the HST in 1994, this vortex is the first one observed on Neptune in the 21st century.
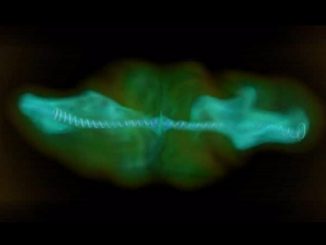
How black hole jets break out of their galaxies
A computer simulation of the powerful jets generated by supermassive black holes at the centres of the largest galaxies explains why some burst forth as bright beacons visible across the universe, while others fall apart and never pierce the halo of the galaxy. A jet’s hot ionised gas is propelled by the twisting magnetic fields of the central rotating black hole.

Hubble finds universe is expanding faster than expected
When Edwin Hubble discovered nearly 100 years ago that the universe was uniformly expanding in all directions, the finding was a big surprise. Then, in the mid-1990s, another shocker occurred: astronomers found that the expansion rate was accelerating, perhaps due to “dark energy.” Now, the latest measurements of our runaway universe suggest that it is expanding faster than astronomers thought.
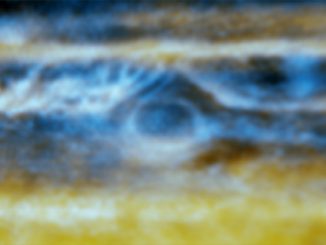
VLA radio map reveals what lies deep below Jupiter’s visible clouds
Observations with the National Science Foundation’s Very Large Array (VLA) have given astronomers an unprecedented look into the atmosphere of Jupiter. The scientists used the VLA to study the dynamics of Jupiter’s atmosphere from the visible cloud surfaces down to about 60 miles (100 kilometres) below the clouds.

Kepler-223 star system has four mini-Neptunes in synchronised orbits
A four-planet system orbiting the star Kepler-223 in the constellation Cygnus is actually a rarity: Its planets, all miniature Neptunes nestled close to the star, are orbiting in a unique resonance that has been locked in for billions of years. For every three orbits of the outermost planet, the second orbits four times, the third six times and the innermost eight times.

Supermassive black hole found in an unlikely place
A near-record 17-billion-solar-mass black hole discovered in a sparse area of the local universe indicates that these monster objects may be more common than once thought. The newly discovered supermassive black hole is in NGC 1600, an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Eridanus some 149 million light-years away.
