
Southwest Research Institute


Hubble spots possible water plumes erupting on Jupiter’s moon Europa
Astronomers using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have imaged what may be water vapour plumes erupting 125 miles (200 kilometres) off the surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa. Europa has a huge global ocean containing twice as much water as Earth’s oceans, but it is protected by a layer of extremely cold and hard ice of unknown thickness.

Most volcanic activity on Mercury stopped about 3.5 billion years ago
New research from North Carolina State University finds that major volcanic activity on the innermost planet most likely ended about 3.5 billion years ago — in stark contrast to the volcanic ages found for Venus, Mars and Earth. These findings add insight into the geological evolution of Mercury and what happens when rocky planets cool and contract.

Freezing effects of Jupiter’s shadow on Io’s volcanic gases revealed
A team of scientists has documented atmospheric changes on Io, Jupiter’s volcanically active satellite, as the giant planet casts its shadow over the moon during daily eclipses. Io’s thin atmosphere collapses as the sulfur dioxide gas emitted from volcanoes freezes when shaded by Jupiter. The atmosphere reforms when Io moves out of eclipse and the ice sublimates.

The case of the missing Ceres craters
Ceres is covered in countless small, young craters, but none are larger than 175 miles (280 kilometres) in diameter. To scientists, this is a huge mystery, given that the dwarf planet must have been hit by numerous large asteroids during its 4.5 billion-year lifetime. Where did all the large craters go?

NASA’s Juno spacecraft closing in on Jupiter for 4 July orbit insertion
On 4 July, NASA will fly a solar-powered spacecraft the size of a basketball court within 2,900 miles of the cloud tops of our solar system’s largest planet, Jupiter. Over the past two weeks, several milestones occurred that were key to a successful 35-minute burn of its rocket motor, which will place the robotic explorer into a polar orbit around the gas giant.

Primordial asteroid impacts a possible solution to “faint young Sun paradox”
In the first billion years of Earth’s history, the planet was bombarded by primordial asteroids, while a faint Sun provided much less heat. A Southwest Research Institute-led team posits that this tumultuous beginning may have ultimately fostered life on Earth, particularly in terms of sustaining liquid water.

Pluto’s “Twilight Zone” reveals its secrets
NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft took this stunning image mere minutes after closest approach on 14 July 2015. Seen here, sunlight filters through and illuminates Pluto’s complex atmospheric haze layers over portions of the nitrogen ice plains informally named Sputnik Planum, as well as mountains of the informally named Norgay Montes.

New Horizons’ best close-up of Pluto’s surface
A mosaic strip just released by the New Horizons team now includes all of the highest-resolution images taken by the NASA probe. The mosaic affords scientists and the public the best opportunity to examine the fine details of the various types of terrain on Pluto, and determine the processes that formed and shaped them.
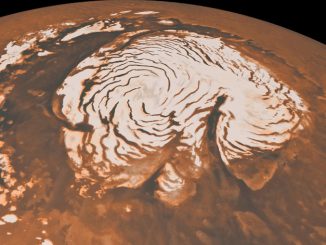
Scientists find evidence of ice age at Mars’ north pole
Using radar data collected by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, researchers have found evidence of an ice age recorded in the polar deposits of Mars. Measurements show that about 87,000 cubic kilometres of ice have accumulated at the poles since the end of the last ice age about 370,000 years ago; the majority of the material accumulated at the Martian north pole.
