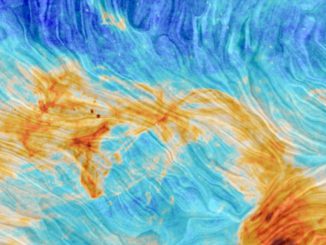
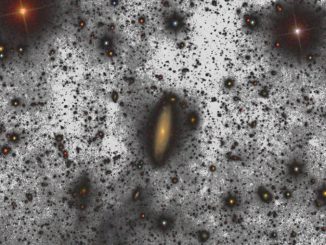
Galactic merger exposes supermassive black hole
Astronomers using the super-sharp radio vision of the National Science Foundation’s Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) have found the shredded remains of a galaxy that passed through a larger galaxy, leaving only the smaller galaxy’s nearly-naked supermassive black hole to emerge and speed away at more than 2,000 miles per second.