
Observing




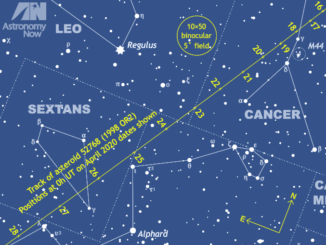
Seek out 1998 OR2, the brightest predicted near-Earth asteroid encounter of 2020
A near-Earth object (NEO) and potentially hazardous asteroid (PHA) with the catchy official name of 52768 (1998 OR2) passes just 16.4 lunar distances (6.3 million kilometres) from Earth at 09:56 UT on Wednesday, 29 April 2020. Here’s our guide to locating this fascinating asteroid in 15-cm (6-inch) aperture telescopes and smaller from the UK this month.

See the waning crescent Moon meet the dawn planets, 15–16 April 2020
There’s a lot of planetary activity in the dawn sky in mid-April. If you’re an early riser in the British Isles, let the waning crescent Moon be your guide to the naked-eye planets Jupiter, Saturn and Mars on 15 and 16 April 2020. Typical 7×50 or 10×50 binoculars will show these attractive conjunctions well, while the smallest of telescopes also reveal some of Jupiter’s bright Galilean moons.

Don’t miss the largest supermoon of 2020 on 8 April
The full Moon of 8 April 2020 occurs just 8½ hours after perigee, its closest point to Earth in the oval-shaped lunar orbit. A full Moon occurring close to perigee is popularly called a supermoon, and this one will be 8½ percent larger than average. This is also the closest full Moon of the year and we’ll not see one larger until 5 November 2025.

Get ready for Comet ATLAS (C/2019 Y4) in the northern spring sky!
Comet C/2019 Y4 was discovered by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) on 28 December last year and brightened 6000-fold in just two months to attain magnitude +7.5 on 1 April. Alas, the comet’s nucleus has now fragmented, dashing hopes for a conspicuous naked-eye spectacle in the constellation of Perseus. Here’s our telescopic observing guide.

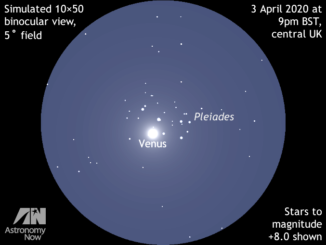
Planet Venus photobombs the Pleiades (Seven Sisters) 1–5 April
As April 2020 opens, dazzling Venus at dusk is drawing ever closer to the magnificent Pleiades (Seven Sisters) in the constellation of Taurus. The brightest planet makes its closest approach to this famous open star cluster on the UK night of 3 April, when typical 10×50 binoculars and small telescopes will deliver memorable views around 9pm BST.
