Very Long Baseline Array



VLA reveals new object near supermassive black hole in famous galaxy
Pointing the Very Large Array at a famous galaxy for the first time in two decades, a team of astronomers got a big surprise, finding that a bright new object had appeared near the galaxy’s core. The object, the scientists concluded, is either a very rare type of supernova explosion or, more likely, an outburst from a second supermassive black hole closely orbiting the galaxy’s primary, central supermassive black hole.

Galactic merger exposes supermassive black hole
Astronomers using the super-sharp radio vision of the National Science Foundation’s Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) have found the shredded remains of a galaxy that passed through a larger galaxy, leaving only the smaller galaxy’s nearly-naked supermassive black hole to emerge and speed away at more than 2,000 miles per second.

Supermassive black hole fed by cold intergalactic downpour
An international team of astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimetre/submillimetre Array (ALMA) has witnessed a cosmic weather event that has never been seen before — a cluster of towering intergalactic gas clouds raining in on the supermassive black hole at the centre of a huge galaxy one billion light-years from Earth.

Space-Earth system produces highest-resolution astronomical image
Using an orbiting radio-astronomy satellite combined with 15 ground-based radio telescopes, astronomers have made the most-detailed astronomical image yet, revealing new insights about a gorging black hole in a galaxy 900 million light-years away. The image has the resolving power of a telescope about 62,500 miles wide, or almost eight times the diameter of the Earth.
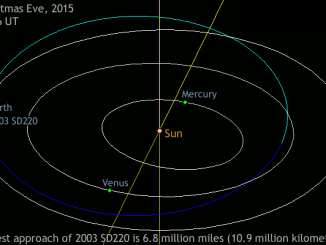
Asteroid 2003 SD220 sleighs by Earth on Christmas Eve
During the month of December, the Planetary Radar Group at Arecibo Observatory has observed near-Earth asteroid 2003 SD220, which will make its closest approach to Earth on Christmas Eve. Although designated as “potentially hazardous,” this asteroid will be 28 times further away than our Moon and therefore poses no present danger to Earth.
