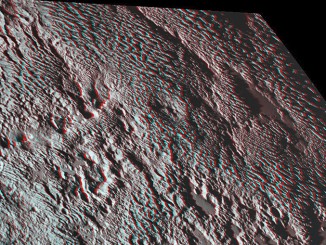
A ‘super Grand Canyon’ on Pluto’s moon Charon
Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, is home to an unusual canyon system that’s far longer and deeper than Arizona’s Grand Canyon. As far as NASA’s New Horizons scientists can tell, the canyon informally named Argo Chasma has a total length of approximately 430 miles — one and a half times the length and five times the depth of the Grand Canyon on Earth.