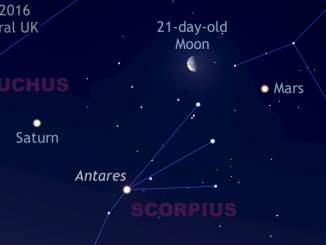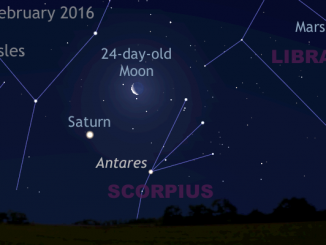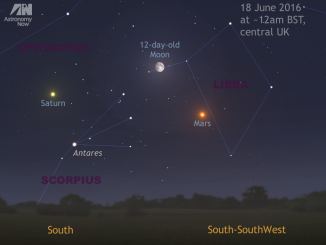
See the Moon’s midnight rendezvous with Mars and Saturn
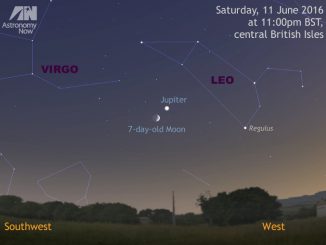
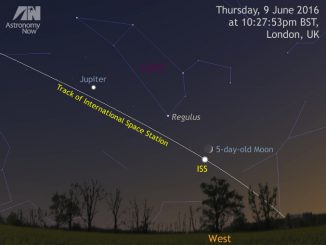
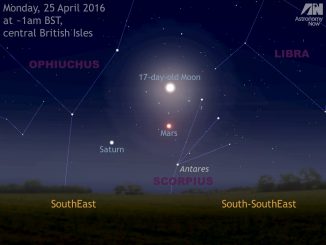
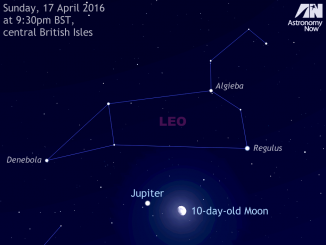
We may be losing Jupiter in the west at dusk, but two other planets are well placed in the late evening. Skywatchers in the UK and Western Europe should look low in the southern sky around 12am local time on 17, 18 and 19 June to see the waxing gibbous Moon in the vicinity of planets Mars and Saturn, plus first-magnitude star Antares in the constellation of Scorpius.