
Charon



A new perspective on how Pluto’s “icy heart” came to be
Pluto’s “icy heart” is a bright, two-lobed feature on its surface that was discovered by NASA’s New Horizons team in 2015. The heart’s western lobe, informally named Sputnik Planitia, is a deep basin generally thought to have been created by a smaller body striking Pluto at extremely high speed, but a new study suggests a different origin.

New analysis supports subsurface ocean on Pluto
A liquid ocean lying deep beneath Pluto’s frozen surface is the best explanation for features revealed by NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, according to a new analysis. The idea that Pluto has a subsurface ocean is not new, but the study provides the most detailed investigation yet of its likely role in the evolution of key features such as the vast, low-lying plain known as Sputnik Planitia (formerly Sputnik Planum).

Pluto ‘paints’ its largest moon red
In June 2015, when the cameras on NASA’s approaching New Horizons spacecraft first spotted the large reddish polar region on Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, mission scientists knew two things: they’d never seen anything like it elsewhere in our Solar System, and they couldn’t wait to get the story behind it.

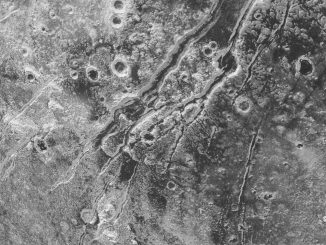
A ‘super Grand Canyon’ on Pluto’s moon Charon
Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, is home to an unusual canyon system that’s far longer and deeper than Arizona’s Grand Canyon. As far as NASA’s New Horizons scientists can tell, the canyon informally named Argo Chasma has a total length of approximately 430 miles — one and a half times the length and five times the depth of the Grand Canyon on Earth.
Pluto could still have a liquid sub-surface ocean
NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft spied extensional faults on Pluto, a sign that the dwarf planet has undergone a global expansion possibly due to the slow freezing of a sub-surface ocean. A new analysis by Brown University scientists bolsters that idea, and suggests that ocean is likely still there today.

Close encounters of a tidal kind could lead to cracks on icy moons
A new model developed by University of Rochester researchers could offer an explanation as to how cracks on icy moons, such as Pluto’s Charon, formed. Until now, it was thought that the cracks were the result of geodynamical processes, such as plate tectonics, but computer simulations suggest that a close encounter with another body might have been the cause.

Hubble discovers moon orbiting the dwarf planet Makemake
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has spotted a small, dark moon orbiting Makemake, the second brightest icy dwarf planet — after Pluto — in the Kuiper Belt. The moon, provisionally designated S/2015 (136472) 1 and nicknamed MK 2, is estimated to be 100 miles in diameter. Makemake and its moon are more than 50 times farther away than Earth is from the Sun.

Did Pluto’s moon Charon possess an ancient subsurface ocean?
This image from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft focuses on a section of the informally named Serenity Chasma, part of a vast equatorial belt of chasms on Pluto’s largest moon, Charon. Scientists believe that Charon’s subsurface water-ice layer may have been partially liquid in its early history, and has since refrozen, expanded and pushed the surface outward, producing the massive chasms we see today.
