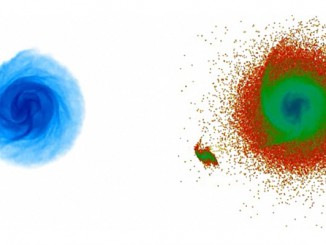
Galaxy quakes could improve hunt for dark matter
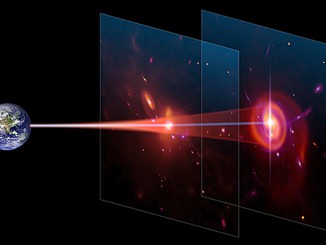
Ripples in gas at the outer disc of our galaxy have puzzled astronomers since they were first revealed by radio observations a decade ago. Now, astronomers believe they have found the culprit — a dwarf galaxy, containing dark, unseen material, which skimmed the outskirts of the Milky Way a few hundred million years ago. This method to characterise dark matter marks first real application of galactoseismology.